2024 AI In The Workforce Survey: Insights on Generative Artificial Intelligence and Perceptions and Expectations Among Professionals
UK workers have a complex relationship with generative AI and it\'s only getting more complex.
The Covelent Workforce Survey, conducted over Q4 2023, involved 2,113 professionals across various key industries, revealing significant insights into the perception of generative artificial intelligence (AI). The findings paint a picture of a professional community at a crossroads. While there is recognition of the potential benefits AI can bring, such as enhanced efficiency and innovation, there is an escalating concern, with 65% of workers apprehensive about the rapid pace of AI development. This fear is rooted in the possibility that their jobs might be automated much sooner than previously anticipated, a sentiment that has markedly grown since the beginning of 2023. The survey sheds light on the urgent need for industries and policymakers to respond to these concerns, ensuring a balanced and ethical integration of AI into the workforce.
Methodology
Engaging 2,113 professionals from across the UK's key sectors, Financial Services (inc. Insurance, Wealth Management, Investment and Retail Banking), Logistics, Manufacturing, Media, Professional Services (inc. Legal Services, Accounting, Advertising, Architects) and Technology. Respondents were split between gender and across age groups, with 13% Generation Z (aged 18-24), 20% younger millennials (25-31), 26% older millennials (32-39), 22% Generation X (40-55) and 19% baby boomers (56-69).The survey was conducted between 28 September to 28 December utilising an online questionnaire and structured telephonic interviews. The responses were analysed to understand the prevailing sentiments about AI's impact on the future of work.
Key Findings
The survey's key findings reveal a landscape of mixed emotions towards AI:
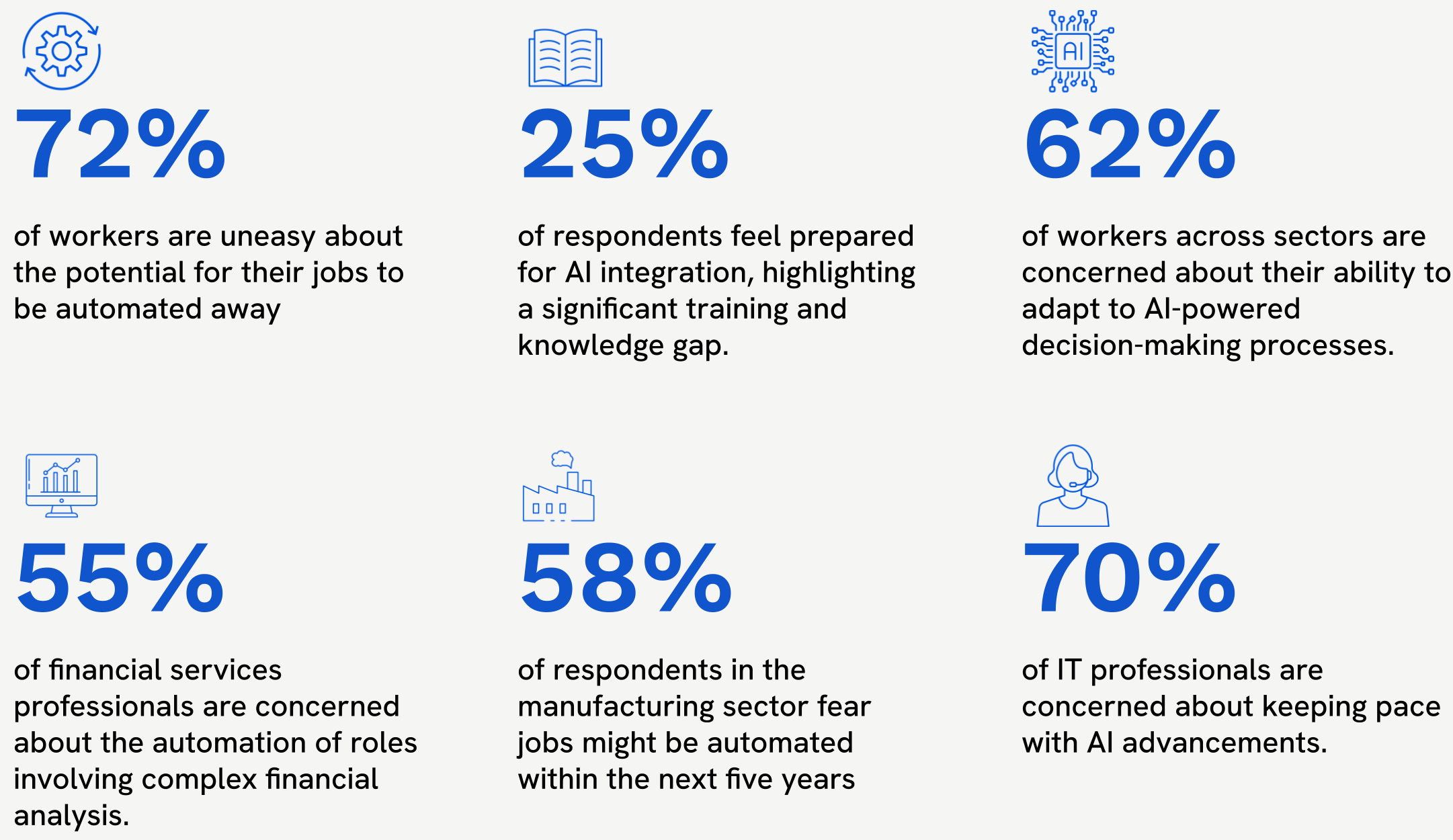
- Rapid Automation Concerns: A significant 65% of the total respondents express unease about the potential for their jobs to be automated away due to the fast-paced development of AI, a concern that was less pronounced at the start of the year.
- Sector-Specific Fears: Concerns vary across sectors, with manufacturing and finance professionals particularly worried about the immediacy of AI-driven job automation.
- Lack of Preparedness: Despite the perceived threat of automation, only 25% of respondents feel prepared for AI integration, highlighting a significant training and knowledge gap.
- Ethical Implications: Ethical considerations, especially in healthcare (e.g., potential for algorithmic bias in medical diagnosis) and finance (e.g., opaqueness of AI-driven investment decisions), have emerged as a significant concern, with professionals worried about the repercussions of rapid AI deployment without adequate ethical frameworks.
- Adaptation to AI-Powered Decision-Making: The survey revealed that 62% of employees across all sectors are concerned about their ability to adapt to AI-powered decision-making processes. Many professionals are apprehensive about relying on AI for critical decisions, fearing a loss of personal judgement and expertise in their roles. This finding is especially pronounced in sectors like finance and healthcare, where decision-making has traditionally been deeply reliant on human expertise.
- AI's influence on diversity: An intriguing aspect of the survey is the mixed sentiment regarding AI's impact on workplace diversity and inclusion, with 48% expressing concerns that AI, if not properly managed, could perpetuate existing biases or create new forms of workplace inequality (e.g., gender bias in recruitment algorithms). These respondents highlighted the need for AI systems to be designed and implemented in a way that actively promotes diversity and counters bias, especially in recruitment and management processes.
Sector-Specific Insights

- Healthcare: While 80% believe AI will revolutionise diagnostics, half of the respondents (50%) are increasingly troubled by the ethical challenges and rapid implementation of AI in patient care.
- Finance: 55% of finance professionals are now concerned about the automation of roles involving complex financial analysis, a scenario that seemed unlikely at the beginning of 2023.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector shows the highest level of concern, with 58% of respondents fearing that their jobs might be automated within the next five years, a significant increase from earlier projections.
- Information Technology: IT professionals, while generally more optimistic about AI, are now faced with the challenge of rapidly evolving job requirements, with 70% expressing concerns about keeping pace with AI advancements.
"The insights gathered from this survey present a compelling narrative about the state of AI in the workplace and how it's been received by our workforces. It's evident that while AI offers opportunities for growth and efficiency, it also brings to the fore substantial challenges that require our immediate attention. The apprehension among professionals regarding the rapid pace of AI and its potential impact on job security is not just a concern for the individual but a call to action for the industry as a whole. It's imperative that we forge a path forward that is grounded in ethical practices, prioritises the upskilling of our workforce, and embraces a collaborative approach.'" comments Covelent Managing Partner Nik Nicholas
The survey highlights a crucial shift in the professional perspective towards AI. The accelerated pace of AI development has not only fostered optimism for innovation but has also intensified concerns about job security and the ethical dimensions of AI in the workplace. This evolving sentiment underscores the need for a more strategic approach in preparing the workforce for an AI-dominated future.
Recommendations - Addressing the Revolution: Four Imperatives for Smooth Integration
The rapid march of AI presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges for businesses and society. While the potential for efficiency gains and innovation is undeniable, concerns about job displacement, ethical implications, and inadequate skills are understandably bubbling to the surface. To harness the potential of AI while mitigating its risks, four key imperatives emerge:
1. Retooling the Workforce: Embracing Upskilling and Reskilling as Core Strategies
The statistic that 70% of employees feel unprepared for AI integration should be a clear call for action. Employers must shift their mindset from viewing AI as a threat to jobs to harnessing it as an opportunity to redefine roles and skillsets. Comprehensive AI-related training programs are no longer a luxury, but a strategic imperative. These programs should go beyond technical education, encompassing the ethical, societal, and practical implications of AI within specific sectors. By investing in their workforce's adaptability, companies can not only address present anxieties but also build a future-proof talent pool equipped to thrive in the AI-powered landscape.
2. Navigating the Moral Maze: Building Trust Through Ethical AI Frameworks
As AI increasingly penetrates fields like healthcare and finance, ethical concerns related to data privacy, transparency, and algorithmic bias demand immediate attention. Policymakers must play a proactive role in establishing robust ethical frameworks for AI development and deployment. These frameworks should not stifle innovation, but rather provide clear guidelines for responsible AI that prioritises fairness, transparency, and accountability. Public engagement and stakeholder dialogue are crucial for building trust and ensuring ethical AI development that benefits all.
3. Charting Sector-Specific Roadmaps: Tailoring AI Integration for a Smooth Transition
The impact of AI will vary significantly across different sectors. While manufacturing may face substantial automation, finance might grapple with AI-driven decision-making processes. For each sector, policymakers and industry leaders must collaborate to develop tailored strategies for AI integration. These strategies should not only aim to maximise the benefits of AI but also actively manage the transition, minimising job displacement and fostering new opportunities. Sector-specific skill gaps must be identified and addressed through targeted training programs, ensuring a smooth and equitable transition for the workforce.
4. Reshaping Education: Equipping the Next Generation for the AI Era
The transformative potential of AI necessitate a critical reimagining of the education landscape. Educational institutions must move beyond simply offering basic digital literacy and delve into the complexities of AI. Curricula should integrate modules on the ethical, societal, and practical applications of AI across various sectors. By equipping students with a holistic understanding of this technology, education can cultivate a generation of informed, responsible, and AI-savvy individuals prepared to lead the way in the years to come.
Addressing these four imperatives will not be easy, but it is crucial. By proactively preparing for the AI revolution, we can ensure that this transformative technology fosters a bright future for businesses, individuals, and society as a whole.
Related Insights
View all
Data Processing Secrets Every Business Needs to Know
Data processing techniques can be used in a wide range of situations, including real-time and batch processing. However, there is a false divide between batch and streaming processing, making it harder for organisations to improve the quality and availability of information. Streaming technology can improve the cost, quality, and availability of data by combining batch and streaming processing, allowing businesses to make better decisions and predict costs in real time. Organisations should use a unified data architecture and combining batch and streaming processing to improve data quality, cost, and access to information. They should also have skilled workers and security measures in place. Evaluate data infrastructure, define data processing needs, implement unified data architecture, invest in employee training, and ensure data security and compliance to maximise benefits of data processing.

Five essential data best practices for data-informed businesses
Businesses must adopt five essential data best practices to ensure data quality, compliance, and security to drive performance and growth. Adopting five essential data best practices can help businesses effectively manage and capitalise on their data assets, driving performance, growth, and customer satisfaction.

Five Imperatives for Executive Boards Considering Investment in Generative AI
As generative AI technologies evolve, executive boards face the imperative of making astute investment decisions to unlock value and ensure sustainable growth. This article outlines five critical considerations: establishing a business case, leveraging data ecosystems, navigating ethical and regulatory landscapes, addressing talent needs, and ensuring scalability and future-readiness. Each imperative is crucial for maximising return on investment and achieving strategic alignment.